Microsoft Excel is one of the most powerful tools for data analysis, reporting, and management. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, knowing key Excel formulas can significantly boost your efficiency. In this blog, we’ll cover some of the most important Excel formulas that you should master.
1. SUM() – Adding Values using excel formulas
The SUM() function helps you quickly add multiple numbers.
Formula:
=SUM(A1:A10)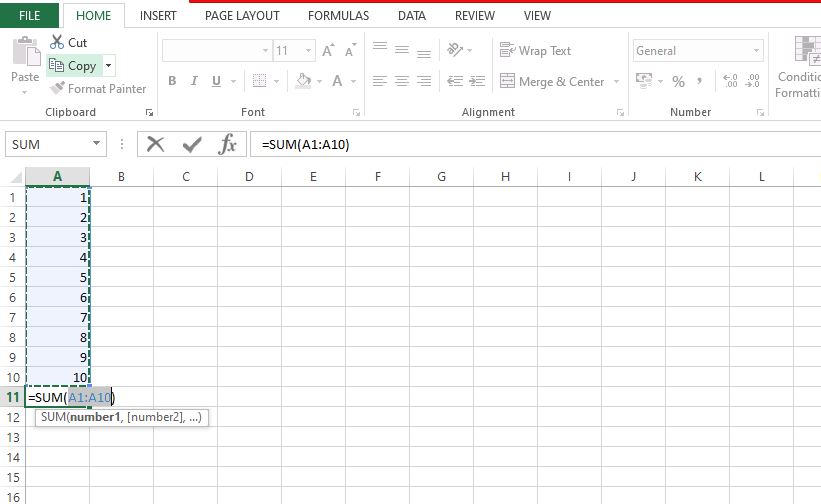
This adds the values from cells A1 to A10.
2. AVERAGE() – Finding the Mean
The AVERAGE() function calculates the arithmetic mean of a range of numbers.
Formula:
=AVERAGE(B1:B10)This returns the average of the numbers in B1 to B10.
3. IF() – Conditional Logic
The IF() function allows you to return different results based on a condition.
Formula:
=IF(A1>50, "Pass", "Fail")If the value in A1 is greater than 50, it returns “Pass”, otherwise “Fail”.
4. VLOOKUP() – Searching for a Value
VLOOKUP() is used to search for a value in a column and return a corresponding value from another column.
Formula:
=VLOOKUP(101, A2:C10, 2, FALSE)This looks for the value 101 in column A and returns the corresponding value from column 2.
5. HLOOKUP() – Horizontal Lookup
Similar to VLOOKUP(), but searches for values in a row instead of a column.
Formula:
=HLOOKUP(50, A1:G3, 2, FALSE)This searches for 50 in the first row and returns the corresponding value from the second row.
6. INDEX() – Returning a Specific Cell Value
INDEX() helps retrieve a value from a given row and column in a range.
Formula:
=INDEX(A2:C5, 2, 3)This fetches the value from row 2, column 3 of the given range.
7. MATCH() – Finding the Position of a Value
MATCH() returns the position of a value in a column or row.
Formula:
=MATCH(45, A1:A10, 0)This finds the position of 45 in the range A1:A10.
8. CONCATENATE() or TEXTJOIN() – Combining Text
CONCATENATE() joins text from multiple cells. A better alternative in modern Excel versions is TEXTJOIN().
Formula:
=TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, A1, B1, C1)This combines values from A1, B1, and C1 with a comma separator.
9. LEFT(), RIGHT(), MID() – Extracting Text
These functions help extract specific parts of text from a cell.
Formula:
=LEFT(A1, 4) // Extracts first 4 characters
=RIGHT(A1, 3) // Extracts last 3 characters
=MID(A1, 2, 5) // Extracts 5 characters starting from position 210. LEN() – Counting Characters
LEN() returns the number of characters (including spaces) in a text string.
Formula:
=LEN(A1)This counts the total number of characters in A1.
11. TRIM() – Removing Extra Spaces
The TRIM() function removes all extra spaces from a text string, leaving only single spaces between words.
Formula:
=TRIM(A1)12. NOW() & TODAY() – Current Date and Time
NOW()returns the current date and time.TODAY()returns only the current date.
Formula:
=NOW()
=TODAY()13. ROUND(), ROUNDUP(), ROUNDDOWN() – Rounding Numbers
ROUND()rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places.ROUNDUP()always rounds up.ROUNDDOWN()always rounds down.
Formula:
=ROUND(A1, 2) // Rounds to 2 decimal places
=ROUNDUP(A1, 2) // Always rounds up to 2 decimal places
=ROUNDDOWN(A1, 2) // Always rounds down to 2 decimal places14. COUNT(), COUNTA(), COUNTIF() – Counting Cells
COUNT()counts numeric values.COUNTA()counts non-empty cells.COUNTIF()counts cells that meet a condition.
Formula:
=COUNT(A1:A10) // Counts numbers
=COUNTA(A1:A10) // Counts all non-empty cells
=COUNTIF(A1:A10, ">50") // Counts numbers greater than 50Conclusion
Mastering these essential Excel formulas will help you work more efficiently and improve your data analysis skills. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, understanding these functions can save you time and effort in handling spreadsheets. Happy Excel-ing!

Pingback: How to Fix Missing Bluetooth on Windows 11: Easy Troubleshooting Guide